View pictures in App save up to 80% data.
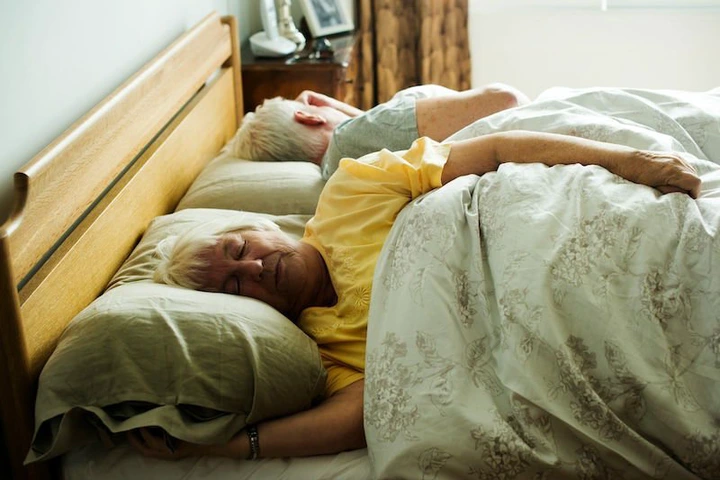
Achieving restful sleep is crucial for overall health. It enhances cognitive abilities, boosts the immune system, and contributes to cardiovascular wellness.
Conversely, issues with sleep such as insomnia and sleep apnea can result in significant health complications and may elevate the risk of neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease. Insufficient sleep is frequently an early indicator of ailments like dementia, highlighting the importance of recognizing the ways in which sleep supports brain health.
New research published in Cell sheds light on how the brain clears harmful waste during sleep. For the first time, scientists have identified a coordinated process during non-REM sleep in mice involving the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, cerebral blood flow, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
These coordinated waves stimulate the glymphatic system, a complex network responsible for eliminating waste from the brain, such as proteins like amyloid and tau that are associated with neurodegenerative disorders.
Exploring the Brain's Waste Clearance Mechanism
During sleep, the brain shifts from handling external stimuli to prioritizing internal upkeep, including the removal of waste products.
Maiken Nedergaard, MD, DMSc, co-director of the University of Rochester Center for Translational Neuromedicine, states that the elimination of waste is essential for maintaining brain health, which could shed light on the restorative benefits of sleep.
The research indicated that norepinephrine is crucial in this mechanism. This neurotransmitter, often linked to alertness and stress response, facilitates the formation of slow, synchronized waves during non-REM sleep.
These waves, referred to as "micro-arousals," lead to the rhythmic constriction of blood vessels in the brain, a phenomenon known as vasomotion. This activity creates the necessary pumping action to facilitate the movement of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through the glymphatic system, aiding in the removal of waste.
A Significant Advancement in Sleep Study
The scientists employed a sophisticated method known as flow fiber photometry, along with various monitoring instruments, to investigate the brain activity of freely roaming mice while they experienced natural sleep and wakefulness.
In contrast to previous research that utilized anesthetized mice in a restrained position, this approach enabled researchers to monitor continuous brain function in a more organic environment.
The research addressed a significant void in our comprehension of the glymphatic system. It was discovered that norepinephrine plays a crucial role in initiating these slow waves and micro-arousals, which has been termed the “missing link” in the system's operation. “These results offer a more detailed understanding of the brain's mechanisms at work during sleep,” remarked Natalie Hauglund, Ph.D., the lead author of the study.
Sleep Aids and Their Unseen Dangers
The study also explored the impact of the sleep medication zolpidem, which is widely recognized by its brand name Ambien.
Although the medication aided mice in achieving sleep, it interfered with the normal fluctuations of norepinephrine, hindering the proper functioning of the glymphatic system. This disruption in the brain's waste removal process might eventually result in neurological problems.
This brings to light worries regarding the extended use of medication for sleep. "It is essential to protect the natural structure of sleep to ensure the health of the brain," stated Nedergaard.
The research indicates that although sleep aids can help alleviate the symptoms of insomnia, they might unintentionally heighten the risk of neurodegenerative disorders by inhibiting essential brain activities.
Taking a Step Towards Improved Sleep Solutions
This study underscores the significance of natural sleep in maintaining brain health and paves the way for innovative methods to enhance sleep quality. By focusing on the dynamics of norepinephrine and other intrinsic processes, researchers could create therapies that promote better sleep while preserving its restorative qualities.
To summarize, this research offers essential information on the process by which sleep removes toxins from the brain and highlights the potential dangers of using specific sleep medications. It stresses the importance of obtaining natural, uninterrupted sleep to safeguard brain health and avert chronic neurological problems.
If you care about Alzheimer’s, please read studies about the likely cause of Alzheimer’s disease and new non-drug treatment that could help prevent Alzheimer’s.
For more information about brain health, please see recent studies about diet that may help prevent Alzheimer’s, and results showing some dementia cases could be prevented by changing these 12 things.
The research findings can be found in Cell.